Why I Won't Vax
Vaxxed vs. Unvaxxed, who is healthier?
The CDC admits they have never conducted a study on fully vaccinated versus fully unvaccinated to compare overall health outcomes. The argument is that it would be "unethical" to withhold vaccines from individuals when a vaccine does exist. A strange argument considering vaccines are withheld from those involved in the safety studies done by the manufacturers prior to licensing. Except in these studies the individuals in the control groups are given the vaccine minus the antigen component or injections of toxic substances such as aluminum. (See Inadequate Safety Testing).
Also, the CDC has the medical records for millions of Americans that could be used to compare the health outcomes without having to withhold vaccines from anyone. They still refuse to do the study.
However, studies by independant doctors and scientists have been done. Here are some of the findings.

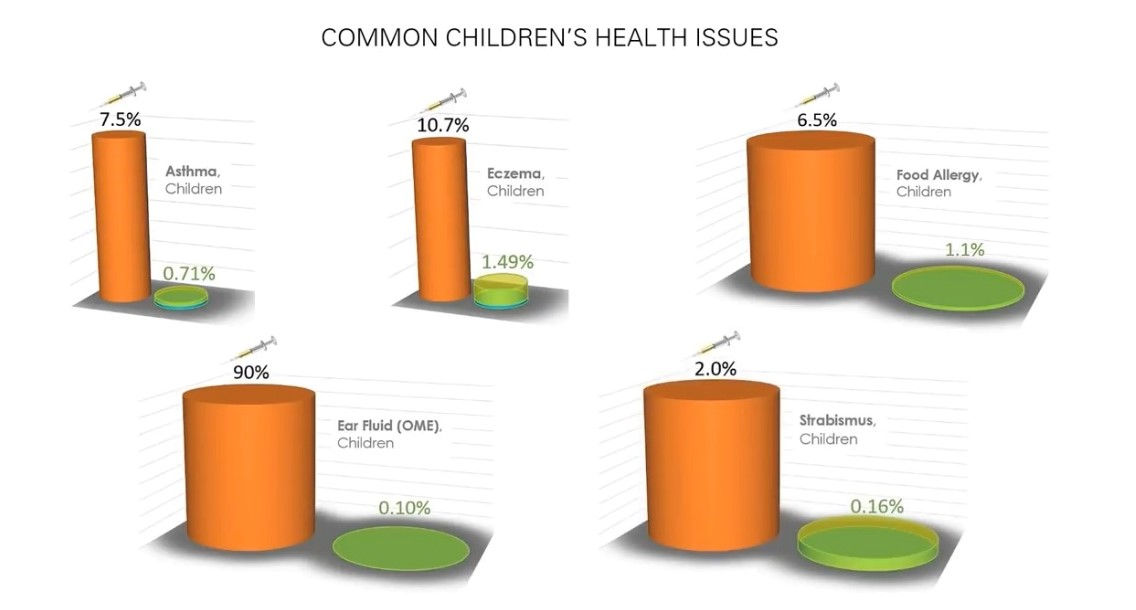
From ICAN
CDC CONCEDES IT HAS NEVER CONDUCTED STUDY OF VACCINATED VS. UNVACCINATED CHILDREN
On July 29, 2020, after months of false claims and objections, the CDC finally conceded that it could not find a single study comparing health outcomes between vaccinated and unvaccinated children and that it “has not conducted a study of health outcomes in vaccinated vs unvaccinated populations.”
Data from Dr. Paul's practice, published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health showed the unvaccinated had superior health outcomes when compared to those variably vaccinated or vaccinated according to the Vaccine-Friendly Plan. Since there was essentially no child in Dr Paul's practice who was following the CDC schedule, one would have to compare these health outcomes with the going rates in America as most in the US vaccinate according to the CDC schedule.
Vaxxed vs. Unvaxxed Studies
What do they show?
(Slides from Children's Health Defense)
February 1, 2004
Frank DeStefano 1, Tanya Karapurkar Bhasin, William W Thompson, Marshalyn Yeargin-Allsopp, Coleen Boyle
Age at first measles-mumps-rubella vaccination in children with autism and school-matched control subjects: a population-based study in metropolitan atlanta
Vaccination before 36 months was more common among case children than control children, especially among children 3 to 5 years of age,

Vaccination before 36 months was more common among case children than control children, especially among children 3 to 5 years of age,

Vaccination before 36 months was more common among case children than control children, especially among children 3 to 5 years of age,
November 1, 2010
Carolyn M Gallagher 1, Melody S Goodman
Hepatitis B vaccination of male neonates and autism diagnosis, NHIS 1997-2002
Boys vaccinated as neonates had threefold greater odds for autism diagnosis compared to boys never vaccinated or vaccinated after the first month of life.

Boys vaccinated as neonates had threefold greater odds for autism diagnosis compared to boys never vaccinated or vaccinated after the first month of life.

Boys vaccinated as neonates had threefold greater odds for autism diagnosis compared to boys never vaccinated or vaccinated after the first month of life.
December 1, 2018
David A. Geier,1,2 Janet K. Kern,1,2,3,* and Mark R. Geier1,2
Premature Puberty and Thimerosal-Containing Hepatitis B Vaccination: A Case-Control Study in the Vaccine Safety Datalink
It was also found that the Hg exposure from Thimerosal-containing hepatitis B vaccines and the risk of being diagnosed with premature puberty occurred primarily in females where both the timing of administration and dose-dependence were important to modifying the effects observed.

It was also found that the Hg exposure from Thimerosal-containing hepatitis B vaccines and the risk of being diagnosed with premature puberty occurred primarily in females where both the timing of administration and dose-dependence were important to modifying the effects observed.

It was also found that the Hg exposure from Thimerosal-containing hepatitis B vaccines and the risk of being diagnosed with premature puberty occurred primarily in females where both the timing of administration and dose-dependence were important to modifying the effects observed.
April 24, 2017
Anthony R Mawson
Azad Bhuiyan
Binu Jacob
Brian D Ray
Pilot comparative study on the health of vaccinated and unvaccinated 6- to 12- year old U.S. children
With regard to acute and chronic conditions, vaccinated children were significantly less likely than the unvaccinated to have had chickenpox and pertussis but, contrary to expectation, were significantly more likely to have been diagnosed with otitis media, pneumonia, allergic rhinitis, eczema, and NDD.

With regard to acute and chronic conditions, vaccinated children were significantly less likely than the unvaccinated to have had chickenpox and pertussis but, contrary to expectation, were significantly more likely to have been diagnosed with otitis media, pneumonia, allergic rhinitis, eczema, and NDD.

With regard to acute and chronic conditions, vaccinated children were significantly less likely than the unvaccinated to have had chickenpox and pertussis but, contrary to expectation, were significantly more likely to have been diagnosed with otitis media, pneumonia, allergic rhinitis, eczema, and NDD.
May 27, 2020
Brian S Hooker1 and Neil Z Miller2
Analysis of health outcomes in vaccinated and unvaccinated children: Developmental delays, asthma, ear infections and gastrointestinal disorders
higher ORs were observed within the vaccinated versus unvaccinated group for developmental delays, asthma and ear infections.

higher ORs were observed within the vaccinated versus unvaccinated group for developmental delays, asthma and ear infections.

higher ORs were observed within the vaccinated versus unvaccinated group for developmental delays, asthma and ear infections.
February 26, 2013
Elizabeth Miller 1, Nick Andrews, Lesley Stellitano, Julia Stowe, Anne Marie Winstone, John Shneerson, Christopher Verity
Risk of narcolepsy in children and young people receiving AS03 adjuvanted pandemic A/H1N1 2009 influenza vaccine: retrospective analysis
The increased risk of narcolepsy after vaccination with ASO3 adjuvanted pandemic A/H1N1 2009 vaccine indicates a causal association, consistent with findings from Finland.

The increased risk of narcolepsy after vaccination with ASO3 adjuvanted pandemic A/H1N1 2009 vaccine indicates a causal association, consistent with findings from Finland.

The increased risk of narcolepsy after vaccination with ASO3 adjuvanted pandemic A/H1N1 2009 vaccine indicates a causal association, consistent with findings from Finland.
April 1, 2003
J B Classen 1, D C Classen
Clustering of cases of type 1 diabetes mellitus occurring 2-4 years after vaccination is consistent with clustering after infections and progression to type 1 diabetes mellitus in autoantibody positive individuals
The current findings indicate the there are also clusters of cases of T1DM occurring 2-4 years post-immunization with the pertussis, MMR, and BCG vaccine. The data are consistent with the occurrence of clusters following mumps infection and the progression to T1DM in patients with antipancreatic autoantibodies.

The current findings indicate the there are also clusters of cases of T1DM occurring 2-4 years post-immunization with the pertussis, MMR, and BCG vaccine. The data are consistent with the occurrence of clusters following mumps infection and the progression to T1DM in patients with antipancreatic autoantibodies.

The current findings indicate the there are also clusters of cases of T1DM occurring 2-4 years post-immunization with the pertussis, MMR, and BCG vaccine. The data are consistent with the occurrence of clusters following mumps infection and the progression to T1DM in patients with antipancreatic autoantibodies.
January 8, 2019
David A Geier,1,2 Janet K Kern,1,2 and Mark R Geier1,2
A cross-sectional study of the relationship between reported human papillomavirus vaccine exposure and the incidence of reported asthma in the United States
The results in this study provide the first epidemiological evidence supporting the hypothesis that reported HPV vaccine exposure significantly increased the risk of reported incident asthma. A significant association between reported HPV vaccine exposure and reported incident asthma was observed in temporal clustering, survey logistic, and survey frequency modeling even when considering covariates such as age, gender, race, and socioeconomic status. I

The results in this study provide the first epidemiological evidence supporting the hypothesis that reported HPV vaccine exposure significantly increased the risk of reported incident asthma. A significant association between reported HPV vaccine exposure and reported incident asthma was observed in temporal clustering, survey logistic, and survey frequency modeling even when considering covariates such as age, gender, race, and socioeconomic status. I

The results in this study provide the first epidemiological evidence supporting the hypothesis that reported HPV vaccine exposure significantly increased the risk of reported incident asthma. A significant association between reported HPV vaccine exposure and reported incident asthma was observed in temporal clustering, survey logistic, and survey frequency modeling even when considering covariates such as age, gender, race, and socioeconomic status. I
March 17, 2017
Søren Wengel Mogensen,a,1 Andreas Andersen,b,1 Amabelia Rodrigues,a Christine S Benn,b,c and Peter Aabya,b,⁎
The Introduction of Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis and Oral Polio Vaccine Among Young Infants in an Urban African Community: A Natural Experiment
DTP was associated with increased mortality; OPV may modify the effect of DTP.

DTP was associated with increased mortality; OPV may modify the effect of DTP.

DTP was associated with increased mortality; OPV may modify the effect of DTP.
April 24, 2017
Anthony R Mawson
Azad Bhuiyan
Binu Jacob
Brian D Ray
Preterm birth, vaccination and neurodevelopmental disorders: a cross-sectional study of 6- to 12-year-old vaccinated and unvaccinated children
In our initial report [48], logistic regression analyses revealed that both preterm birth and vaccination (receipt of one of more of the recommended vaccines) were significantly associated with NDD after controlling for other factors, suggesting independent effects. However, in a final regression model with interaction, preterm birth combined with vaccination was associated with a 6.6-fold increased odds of NDD, suggesting a synergistic effect. Vaccination was found to be significantly and independently associated with NDD, whereas preterm birth without vaccination was not. However, vaccination coupled with preterm birth greatly increased the odds of NDD over that of vaccination alone, especially compared to being born at term and unvaccinated, suggesting that vaccination may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants.

In our initial report [48], logistic regression analyses revealed that both preterm birth and vaccination (receipt of one of more of the recommended vaccines) were significantly associated with NDD after controlling for other factors, suggesting independent effects. However, in a final regression model with interaction, preterm birth combined with vaccination was associated with a 6.6-fold increased odds of NDD, suggesting a synergistic effect. Vaccination was found to be significantly and independently associated with NDD, whereas preterm birth without vaccination was not. However, vaccination coupled with preterm birth greatly increased the odds of NDD over that of vaccination alone, especially compared to being born at term and unvaccinated, suggesting that vaccination may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants.

In our initial report [48], logistic regression analyses revealed that both preterm birth and vaccination (receipt of one of more of the recommended vaccines) were significantly associated with NDD after controlling for other factors, suggesting independent effects. However, in a final regression model with interaction, preterm birth combined with vaccination was associated with a 6.6-fold increased odds of NDD, suggesting a synergistic effect. Vaccination was found to be significantly and independently associated with NDD, whereas preterm birth without vaccination was not. However, vaccination coupled with preterm birth greatly increased the odds of NDD over that of vaccination alone, especially compared to being born at term and unvaccinated, suggesting that vaccination may adversely affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants.
August 13, 2015
Guillaume Pineton de Chambrun 1, Luc Dauchet 2, Corinne Gower-Rousseau 3, Antoine Cortot 3, Jean-Frédéric Colombel 4, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet 5
Vaccination and Risk for Developing Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Case-Control and Cohort Studies
Subgroup analysis for Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) found an association between the poliomyelitis vaccine and risk for developing CD (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.12-4.63) or UC (RR, 3.48; 95% CI, 1.2-9.71).

Subgroup analysis for Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) found an association between the poliomyelitis vaccine and risk for developing CD (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.12-4.63) or UC (RR, 3.48; 95% CI, 1.2-9.71).

Subgroup analysis for Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) found an association between the poliomyelitis vaccine and risk for developing CD (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.12-4.63) or UC (RR, 3.48; 95% CI, 1.2-9.71).
June 1, 2012
Benjamin J Cowling 1, Vicky J Fang, Hiroshi Nishiura, Kwok-Hung Chan, Sophia Ng, Dennis K M Ip, Susan S Chiu, Gabriel M Leung, J S Malik Peiris
Increased risk of noninfluenza respiratory virus infections associated with receipt of inactivated influenza vaccine
TIV recipients had an increased risk of virologically-confirmed non-influenza infections

TIV recipients had an increased risk of virologically-confirmed non-influenza infections

TIV recipients had an increased risk of virologically-confirmed non-influenza infections